The Ultimate Guide to Laser Engraving Stamps
- Home
- >
- Choose by Industries
- >
- The Ultimate Guide to Laser Engraving Stamps

Laser engraving stamps have come a long way from traditional hand carving and mold-based techniques. Today, with the advancement of laser technology, creating custom stamps has become faster, more precise, and highly versatile.
Whether you’re producing business seals, personal stamps, or artistic designs, laser machines offer an innovative solution that simplifies the entire process.
In this article, we’ll walk you through traditional methods, explore how laser engraving has revolutionized the stamp industry, and guide you step-by-step on how to make your own rubber stamp with laser machine.
1. Traditional Methods of Stamp Making
Hand Carving
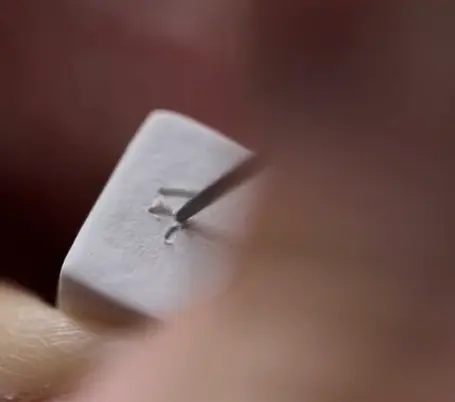


Metal Engraving
Vulcanization
Hot Pressing Molding

2. How Laser Machines Work in Stamp Making


3. Best Materials for Laser Engraving Stamps
- Rubber: Special laser engravable rubber is commonly used for making custom made rubber stamps. It engraves cleanly and produces clear impressions.
- Polymer: Photopolymer plates can be used for creating stamps, especially in a digital workflow.
- Wood: Hardwood or MDF can be engraved to create a stamp, though it may not be as durable as rubber.
- Acrylic: While not as common, acrylic can be used to make durable stamps.
- Leather: Engraved leather can be used for custom stamps, particularly for crafts and artistic purposes.
4. Advantages of Using Laser Machines in Stamp Making
When it comes to stamp making, laser machines offer a range of advantages that enhance precision, speed, customization, and durability—making them an ideal solution for both personal and professional use.
4.1. High Precision
4.2. Efficiency
4.3. Customization
4.4. Anti-counterfeiting
4.5. Durability
5. Types of Customization Stamps
• Rubber Stamps
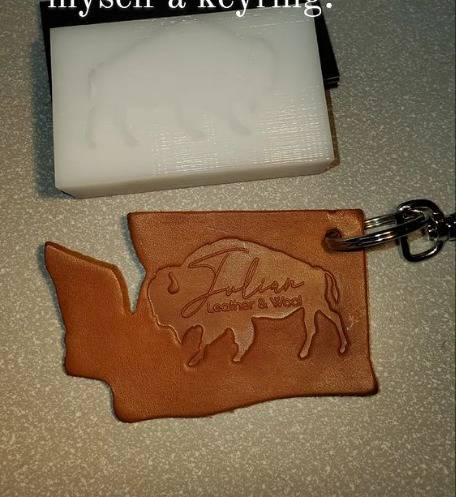


• POM Stamps
Special etching methods create complex, leather stamp pattern.
• Metal Stamps
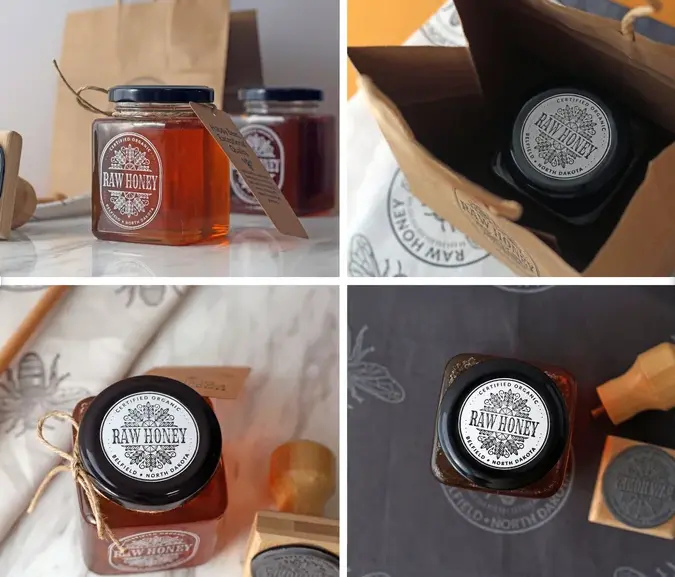
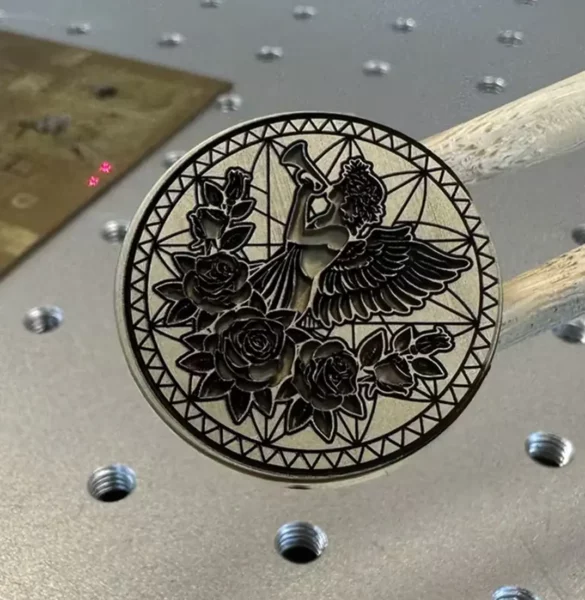

• Personalized Stamps
6. How to Make Your Own Rubber Stamp
Step 1: Create your stamp design
Step 2: Select Appropriate Parameters
Step 3: Confirm parameters to achieve the desired effect
Step 4: Group and mirror the design file, with the blue layer representing the illuminated part
Step 5: Choose single or bidirectional filling, noting that one-way filling yields better results
Step 6: Set DPI to 300 for deeper carving
Step 7: Send the File to the Laser Machine
Step 8: Place the Rubber Stamp Board and Select the File
Step 9: Focus Properly and Start Carving
For more details, you can refer to this guide on how to use a laser engraver to make your own rubber stamp
7. Where to Buy the Materials of Laser Engraving Stamps?
- • Johnson Plastics Plus: https://www.jpplus.com/
- • JDS Industries: https://browse.jdsindustries.com/
- • Amazon: https://www.amazon.com/ref=nav_logo
Conclusion
With the help of laser engraving machines, stamp making is no longer limited by traditional molds or manual craftsmanship. You can now create detailed, durable, and fully customized stamps in a matter of minutes.
Whether you’re crafting stamps for business, branding, or creative purposes, laser technology makes the process more accessible and efficient than ever. Ready to get started? Choose your materials, upload your design, and let the laser machine finish the task.


.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Česká
Česká
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Romania
Romania
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ジャパン
ジャパン
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa