Introduction
Industrial laser cutting machines have revolutionized the way manufacturers process materials across various industries. By using a high-powered laser beam, these machines offer unmatched precision, speed, and efficiency compared to traditional cutting methods. Whether you’re working with metal, plastic, or composite materials, the right laser cutter can significantly enhance your production quality.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through how laser cutting machines work, explore different types like CO₂ and fiber lasers, and help you choose the right one for your specific needs.
1. What is an Industrial Laser Cutting Machine
An industrial laser cutting machine is a versatile and powerful tool used to cut through a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and glass. It operates by using a high-powered laser beam to heat the material being cut, causing it to vaporize or melt. This method of cutting offers numerous advantages over traditional techniques like water jet or plasma cutting.
One of the primary benefits of laser cutting is its ability to produce cleaner, more precise cuts. The concentrated laser beam ensures minimal material distortion, which is especially important in applications where accuracy is crucial, such as in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Furthermore, laser cutters are capable of cutting through thicker materials than other cutting machines, making them ideal for complex projects that demand high precision and strength.
Laser cutting machines are available in various sizes and power levels, allowing users to choose the best option based on the materials they plan to cut and the type of projects they will undertake. When purchasing a laser cutter for a home workshop or business, it’s important to consider features like the ability to connect to a computer for design files, different cutting modes, and options for automatic or manual operation.
2. How Does a Laser Cutting Machine Work?
Understanding how a laser cutting machine works can help you maximize its potential. Most modern laser cutters are controlled by computer software, which allows you to input your desired design and automate the cutting process. Below is a simplified breakdown of how these machines operate:
2.1. Generating a High-Powered Laser Beam
The laser cutting machine typically uses a carbon dioxide (CO2) laser, which generates an infrared beam. This laser beam is then amplified and focused for use in the cutting process.
2.2. Focusing the Laser Beam on the Cutting Area
The laser beam is directed towards the material using a series of mirrors. These mirrors ensure that the beam is accurately focused onto the designated cutting area, ready to begin the process.
2.3. Heating and Vaporizing the Material
Once focused on the material, the high-powered laser heats it to extremely high temperatures. The heat causes the material to either vaporize or melt, depending on its composition. This process allows for precise cutting without much material distortion.
2.4. Following the Laser Cutting Path with Precision
As the laser beam moves along the cutting path, it continues to slice through the material with precision. The machine follows the input design exactly, ensuring that the final cut matches the desired shape and specifications.
2.5. Cooling and Finishing the Material
After the cutting process is completed, the material is cooled down, typically using a stream of compressed air or a coolant system. This cooling step ensures that the material is safe to handle and that the edges of the cut are clean.
3. Choosing the Right Type of Laser Cutter: CO2 vs. Fiber vs. YAG
When shopping for a laser cutter, it’s essential to understand the differences between the most common types of machines. Here’s an overview of the three main types of laser cutters: CO2, Fiber, and YAG, so you can choose the best option for your specific needs.
3.1. CO2 Laser Cutting Machine
CO2 laser cutters are the most commonly used type of laser cutter. These machines are capable of cutting through a wide variety of materials, including plastics, glass, wood and some metals. They come in various sizes and power levels, allowing you to choose a model that suits your cutting requirements.
Features:
– Capable of cutting through a variety of materials
– Available in multiple sizes and power levels
– Some models are compatible with computer software for precise control
3.2. Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
Fiber laser cutters are a newer, more advanced option that offers greater power and precision than CO2 laser cutters. They can cut through thicker materials more efficiently and are generally faster. However, they are also more expensive, which might make them less suitable for those on a budget.
Features:
– More powerful than CO2 laser cutters
– Capable of cutting thicker materials
– Typically more expensive than CO2 laser cutters
3.3. YAG Laser Cutting Machine
YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser cutters are the oldest type of laser cutter. While they are less common than CO2 or fiber laser cutters, they are still used in certain industrial applications. YAG cutters are less powerful and typically used for cutting thinner materials.
Features:
– Less powerful compared to CO2 and fiber lasers
– Suitable for cutting thinner materials
– Less commonly used than CO2 and fiber lasers
Now that you’re familiar with the different types of laser cutters, you can choose the one that best suits your needs. Keep in mind your material requirements, cutting speed, and budget when making your decision. Each type offers unique benefits, so selecting the right one will ensure the best results for your projects.
4. Applications of the Laser Cutting Machine
Laser cutting machines have become essential tools across a wide range of industries due to their precision, efficiency, and versatility. From manufacturing to construction, these machines enable businesses to achieve higher quality, greater speed, and more complex designs. Below are some of the major industries where laser cutting technology plays a critical role.
4.1. Automotive Industry
The automotive industry heavily relies on laser cutting machines for the production of various components. These machines are used to cut intricate parts such as door panels, dashboards, and structural supports with exceptional precision.
Laser cutting also allows for the efficient processing of metal sheets that form car body panels, ensuring both strength and lightweight performance. In addition, manufacturers use laser systems to create detailed logos, emblems, and decorative trims, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of vehicles.
4.2. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, precision and reliability are paramount. Laser cutting machines are utilized to fabricate high-precision components, including aircraft fuselage panels, engine parts, and intricate wing structures.
The minimal heat-affected zones created by laser cutting help preserve the material properties critical to aerospace performance. Advanced design features, such as weight-saving patterns and complex geometries, can be easily achieved, contributing to the efficiency and safety of modern aircraft.
4.3. Construction Industry
The construction industry benefits greatly from the capabilities of laser cutting technology. Laser cutting machines are used to fabricate structural elements such as steel beams, columns, and custom metal panels with remarkable accuracy.
Beyond structural applications, laser cutting enables the creation of intricate architectural details, including decorative facades, balustrades, and metal art installations, helping architects bring complex designs to life while maintaining structural integrity.
4.4. Food and Beverage Industry
Laser cutting technology also finds important applications in the food and beverage industry, particularly in packaging and product marking. Laser systems are used to precisely cut and engrave packaging materials such as plastic films, cardboard, and foil.
In specialized processing lines, lasers can be used to score or lightly slice food products like pastries and confectionery, ensuring consistency and preserving hygiene standards without direct contact.
4.5. Medical Industry
The medical industry demands exceptional precision and quality, making laser cutting machines indispensable. They are widely used to manufacture surgical instruments, implants, and critical medical devices that require clean, precise cuts.
Laser cutting enables the production of miniature components with complex geometries and tight tolerances, which are essential for applications such as stents and orthopedic implants. Additionally, lasers are used for micro-engraving surfaces to improve biocompatibility and functionality.
5. How to Choose a Suitable Industrial Laser Cutting Machine
Selecting the right industrial laser cutting machine is a critical decision for any manufacturer. To ensure you make the best investment, several key factors should be evaluated carefully before making a final choice.
5.1. Understand Your Material Requirements
The first step is to identify the materials you plan to process. This will determine the appropriate laser type — typically a CO₂ laser for non-metallic materials or a fiber laser for metals. Selecting the correct laser source ensures optimal cutting and engraving results.
5.2. Determine the Maximum Material Size
Consider the largest material dimensions you will work with. This will help you select a machine with a suitable bed size and working area. Additionally, factor in the available floor space in your facility to avoid installation challenges.
5.3. Assess Power Needs
Power is a critical specification when choosing a laser machine. Higher power levels enable faster processing speeds and the ability to cut thicker materials. Your power requirements will depend on the maximum thickness of the materials and the production volume you aim to achieve daily.
5.4. Factor in Budget Considerations
Laser machines vary widely in price, depending on power, size, and additional features. Establish a clear budget before you start comparing models. It’s advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure you get the best value without compromising on quality.
5.5. Prioritize Machine Quality and Reliability
Invest in a machine manufactured with high-quality components and a proven track record of reliability. Research reputable brands, read customer reviews, and seek recommendations from industry professionals to make an informed decision.
5.6. Evaluate Bed Size Options
The bed size of the laser machine determines the maximum size of materials you can process. Choose a machine with a bed size that matches your product specifications and production needs. Larger bed sizes offer greater flexibility for various applications.
5.7. Ensure Adequate Cooling and Ventilation
Laser cutting generates significant heat, so proper cooling and ventilation systems are essential. A machine equipped with an efficient cooling system will maintain performance and extend the machine’s service life, while adequate ventilation ensures a safer operating environment.
5.8. Check Software Compatibility
Make sure the laser machine’s software is compatible with your design programs, such as Lightburn software. Easy file transfer between your computer and the machine will streamline workflow and enhance production efficiency.
5.9. Plan for Floor Space Requirements
Laser cutter can occupy considerable space. Carefully measure your available floor area to ensure the machine fits comfortably, with sufficient room for operation, maintenance, and material handling.
5.10. Consider Available Accessories
Some laser cutters come with valuable accessories such as rotary attachments, jigs, and specialized nozzles. Verify which accessories are included and identify any additional tools you may need to purchase separately to maximize your machine’s versatility.
5.11. Review Maintenance Needs
Industrial laser cutters require regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and laser beam alignment. Understanding the machine’s maintenance schedule and requirements will help you plan for minimal downtime and consistent performance.
5.12. Evaluate the Cutting Head Type
Finally, review the type of cutting head the machine offers. Machines with movable cutting heads provide greater flexibility for handling large or complex workpieces. Fixed cutting heads are sufficient for smaller, more uniform tasks.
6. The Best Choice of Laser Cutting Machine
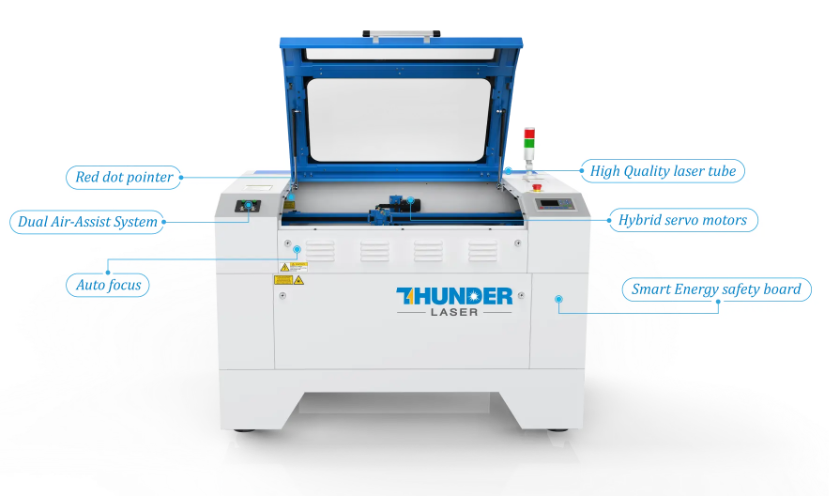
The Nova Laser Cutting Machine is an excellent choice for those looking for a high-performance laser cutter. It is built with high-quality materials, ensuring durability and long-lasting operation. The machine features hybrid servo motors, making it suitable for both small and large jobs.
Its large bed size allows for cutting larger pieces of material with ease. The dual air assist nozzles help prevent heat damage, and the integrated venting system efficiently removes fumes generated during the cutting process, ensuring a cleaner workspace.
One of the standout features of the Nova Laser Cutting Machine is its compatibility with LightBurn software. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, LightBurn’s intuitive interface allows you to design, edit, and control your cutting process seamlessly.
Additionally, the machine supports both Windows and Mac operating systems, providing flexibility for users. Overall, the Nova Laser Cutting Machine is a reliable, versatile, and easy-to-use tool for any laser cutting needs.

Conclusion
Investing in the right industrial laser cutting machine can transform your production capabilities, whether you’re in automotive, aerospace, or custom manufacturing. By understanding how laser cutting works and evaluating the key factors — from material compatibility and machine power to bed size and software support — you can make a well-informed decision.
Whether you choose a CO₂ laser for versatility or a fiber laser for metalworking precision, selecting a reliable, high-quality machine is essential for achieving consistent and professional results.
FAQs about Laser Cutting Machine
Q1. How do I determine the right laser cutter size for my material?
Consider the size and thickness of your materials. Larger bed sizes allow for more flexibility in handling bigger or multiple pieces.
Q2. What factors affect the cutting speed of a laser cutting machine?
Cutting speed depends on laser power, material type, thickness, and the complexity of the cutting path.
Q3. How does cooling affect the performance and longevity of a laser cutter?
Cooling system prevents overheating, ensuring stable performance and extending the machine’s lifespan.
Q4. How do I ensure accurate cuts with a laser cutter?
Proper calibration, maintaining the correct focus, and using suitable materials help ensure accuracy in laser cutting.
Q5. How often should a laser cutting machine be maintained?
Laser cutting machines should be maintained regularly, with cleaning and inspection every 1-3 months. However, critical parts such as the laser lens and mirrors may need cleaning more frequently, depending on usage. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance intervals.

.png) International
International
 United States
United States
 Brasil
Brasil
 Canada
Canada
 Costa Rica
Costa Rica
 Mexico
Mexico
 Česká
Česká
 Romania
Romania
 Polska
Polska
 Ireland
Ireland
 Portugal
Portugal
 Lietuva
Lietuva
 Россия
Россия Deutschland
Deutschland
 Britain
Britain
 Україна
Україна
 France
France
 Sverige
Sverige
 Italia
Italia
 Norway
Norway
 Denmark
Denmark
 Ελλάδα
Ελλάδα
 한국
한국
 中国
中国
 ประเทศไทย
ประเทศไทย
 中国香港
中国香港
 Israel
Israel
 中國臺灣
中國臺灣
 India
India
 پاکستان
پاکستان
 پශ්රී ලංකා
پශ්රී ලංකා
 ジャパン
ジャパン
 Australia
Australia
 New Zealand
New Zealand
 South Africa
South Africa